A Comprehensive Overview of the Bitcoin Ecosystem
2024-04-18
The approval of the Bitcoin ETF has positioned the ecosystem for broader adoption, with increased capital driving innovation. This overview covers inscriptions and the emerging protocols that are expanding Bitcoin's functionality beyond simple payments.
Historical Context
Data inscription on Bitcoin dates back to its inception—Satoshi embedded a newspaper headline in the genesis block. Early attempts included Luke Dash Jr's 2011 Bible verses and the 2013 Bitcoin whitepaper inscription. However, these remained largely unused until the 2021 Taproot upgrade dramatically reduced storage costs, making widespread inscription economically viable.
The Ordinals Protocol
The Ordinals protocol, created by Casey Rodarmor (@rodarmor), introduced a method for storing data efficiently on Bitcoin. Users can now "store any kind of data as code with a cheaper onchain storage price than even Ethereum calldata."
The protocol leverages Taproot scripts—a Bitcoin upgrade from 2021—to enable inexpensive on-chain data storage. This technological advancement made inscriptions economically viable by drastically reducing storage costs, transforming what had previously been impractical into a widespread adoption mechanism.
An important distinction: the Ordinals protocol is the system of ordering sats to create NFTs. Inscriptions are the actual content of these NFTs. The protocol organizes individual satoshis (Bitcoin's smallest unit) while inscriptions represent the actual data embedded within them.
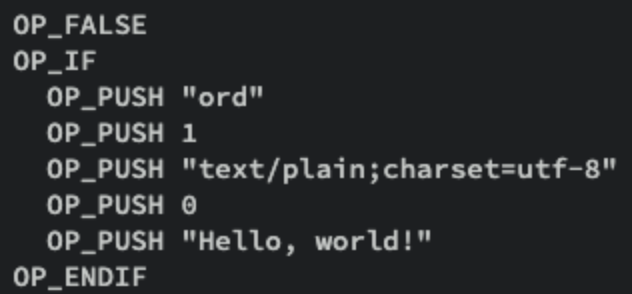
A text inscription example showing "Hello, world!" stored on Bitcoin

Image inscriptions from ordinals.com demonstrating visual content stored on-chain
The Ordinals movement catalyzed a wave of Bitcoin-native assets, including NFT collections like Taproot Wizards and fungible token standards such as BRC-20, fundamentally expanding Bitcoin's application beyond peer-to-peer payments.
BRC-20 Standard
Building on Ordinals, the BRC-20 standard created by @domodata established a fungible token framework on Bitcoin. Users inscribe JSON strings defining token parameters:
{
"p": "brc-20",
"op": "deploy",
"tick": "ordi",
"max": "210,000,000"
}
Off-chain indexers like UniSat explorer and brc-20.io track balances and transactions while maintaining ERC-20-like functionality for minting and transfers.
This approach enables fair distribution through a "proof of wasted blockspace" mechanism, providing equal retail and institutional participation rights without centralized team control—contrasting sharply with typical ERC-20 launches where teams often control large allocations.

The three phases for the creation of a BRC-20 token: Deploy, Mint, and Transfer
Key Technical Advantages
1. Full On-Chain Storage
Unlike ERC-721 NFTs relying on IPFS, inscriptions store both ownership and data directly on-chain. The inscription is stored entirely on-chain, providing complete immutability.
2. Fair Distribution
The mechanism provides equal retail and institutional participation rights without centralized team control.
3. Cost Efficiency
Bitcoin inscription storage costs approximately 7 times less expensive than equivalent Ethereum storage, as noted by Eric Wall in a StarkWare session.
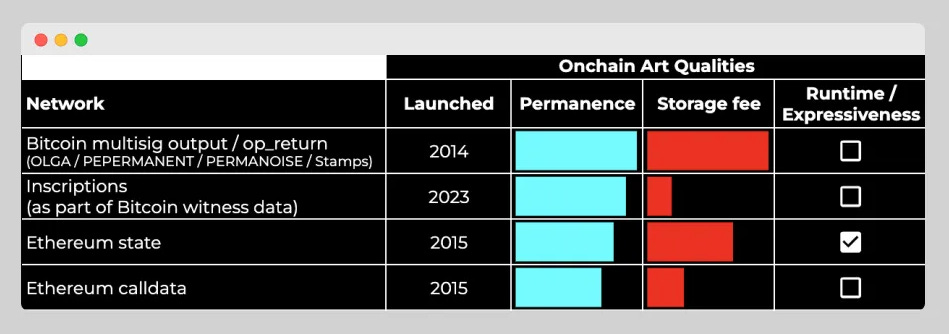
A comparison between different Bitcoin and Ethereum networks on their permanence and storage fees
4. Enhanced Security
Larger transaction sizes and computational complexity increase miner fees, making 51% attacks economically prohibitive. This increased miner revenue strengthens the overall network security.
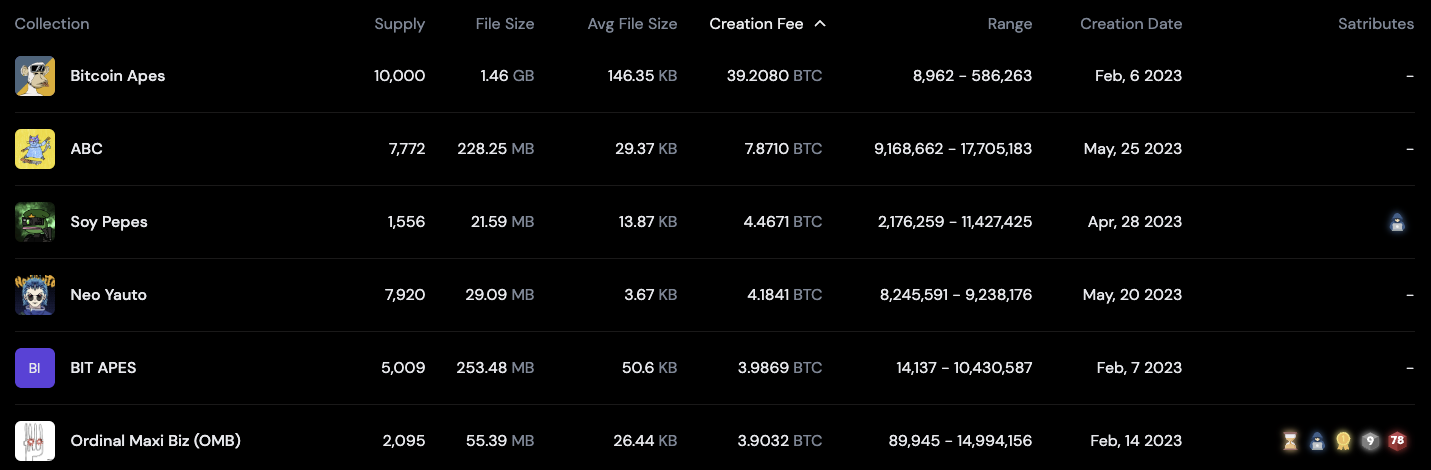
A snapshot of Bitcoin NFTs and their network fees showing increased miner revenue
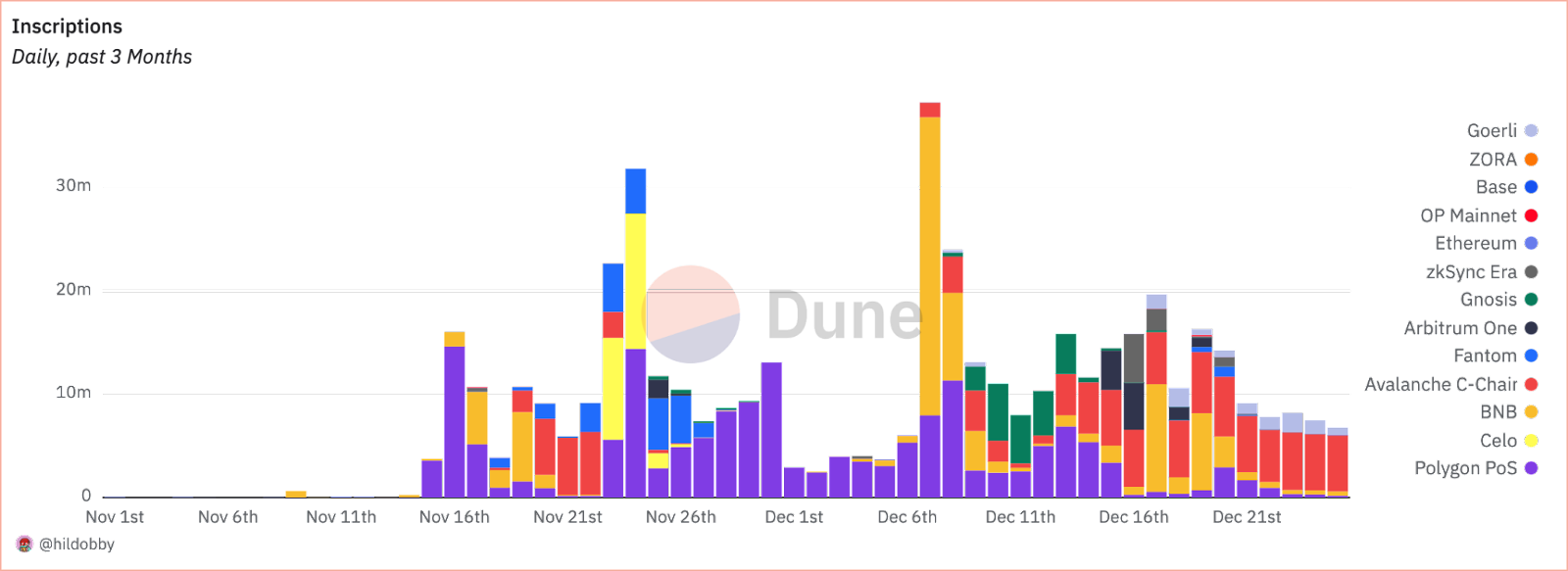
EVM inscriptions activity from various L1s and L2s demonstrating cross-chain adoption
Competing Protocols
Alternative systems emerged addressing Ordinals limitations:
Atomicals
Atomicals is optimized for non-fungible assets with the ARC-20 standard supporting unlimited-length token identifiers, unlike BRC-20's 4-character limit.
Runes
Runes, also created by Casey Rodarmor, is a UTXO-based fungible token protocol emphasizing Bitcoin-like transaction simplicity. It represents a more native approach to fungible tokens on Bitcoin.
PIPE
PIPE combines Runes and BRC-20 concepts with predefined deployment rules, supporting DeFi applications. The Tap Protocol extends this further.
Stamps
Stamps stores data in multisig UTXOs rather than witness data. While more expensive than inscriptions, this approach offers different trade-offs for permanence.
Supporting Ecosystem
Wallets & Marketplaces
OKX Wallet and Unisat dominate trading volume; Magic Eden added Bitcoin NFT support, bringing established marketplace infrastructure to the ecosystem.
Tools
- LooksOrdinal - Deployment interface for creating inscriptions
- Ordiscan - Transaction indexing and exploration
- BRC-20.io - Token visualization and tracking
Infrastructure
- MultiBit - Enables cross-chain swaps between Bitcoin and EVM chains
- Bounce Finance and Turtsat - Operate launchpads for new projects
Market Outlook
Major BRC-20 projects demonstrate significant market interest:
- Ordi reached $1.5B fully-diluted valuation
- Sats achieved $1B fully-diluted valuation
However, these projects lack foundational guidance structures similar to Ethereum or Solana foundations. The communities are largely retail-driven without institutional governance frameworks.
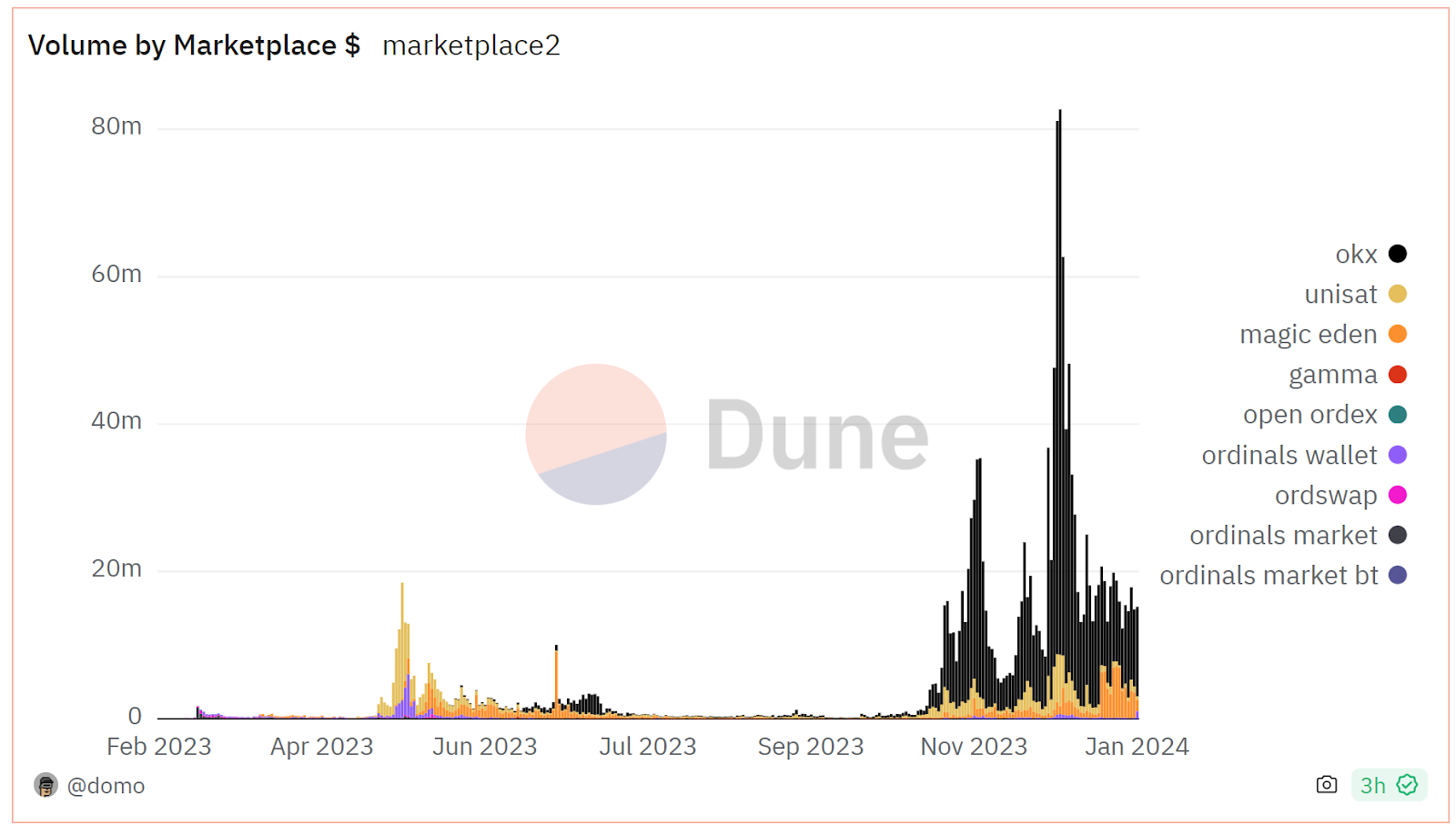
Monthly trading volume for inscription-based assets showing market activity trends
Future Implications
Inscriptions themselves function as a proprietary Layer 2, expanding Bitcoin's functionality beyond simple payments. As institutional adoption increases through vehicles like the Bitcoin ETF, demand for enhanced functionality will likely intensify protocol development and community governance evolution.
The inscription economy has created new use cases for Bitcoin while maintaining the security guarantees of the base chain. This represents a fundamental expansion of what's possible on the world's most secure blockchain network.